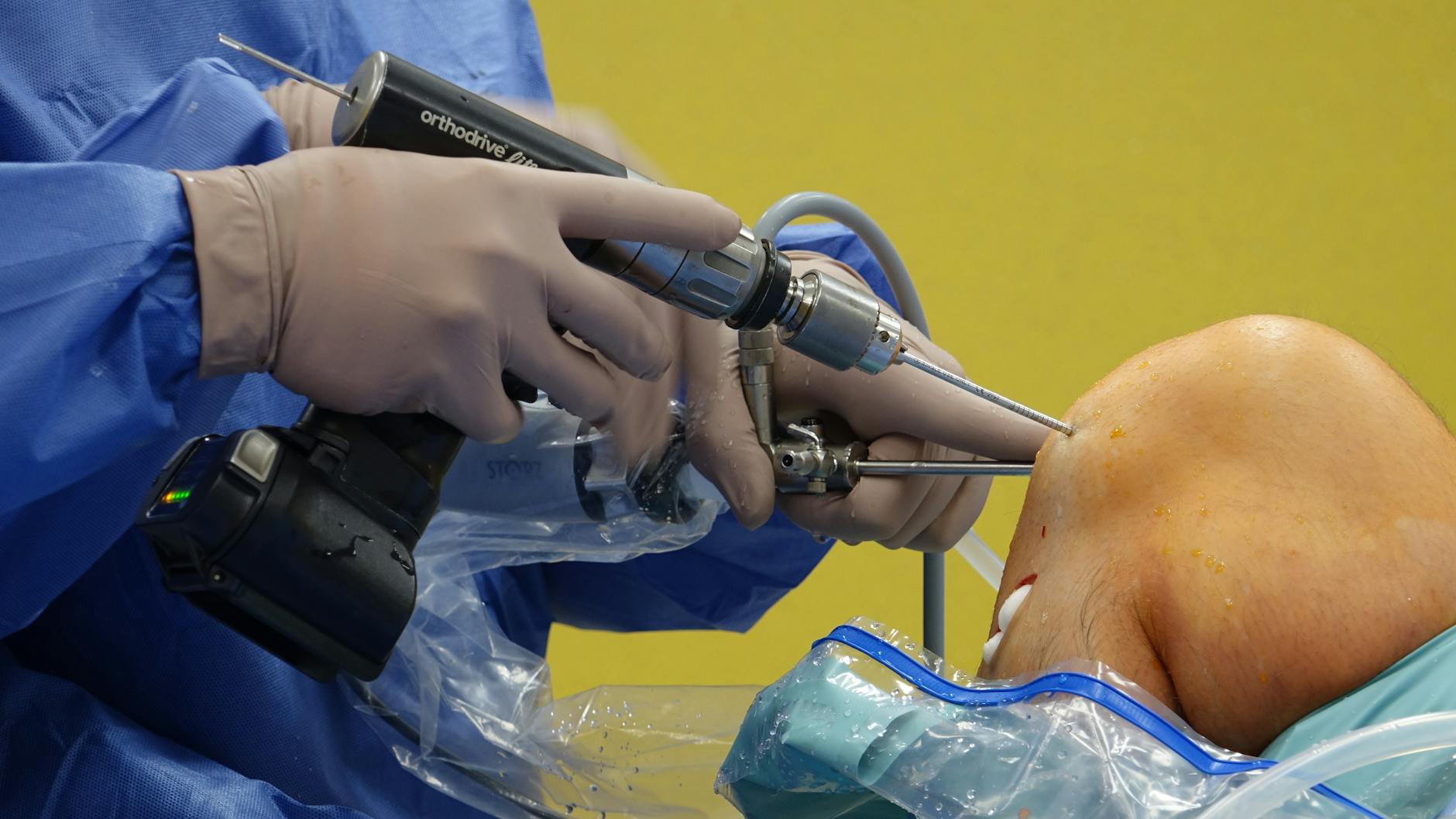
You’ve heard of orthopedic surgeons—but what exactly do they treat?
Orthopedic surgeons are specialists who focus on the musculoskeletal system. This includes bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and nerves. They treat conditions that affect your ability to move, such as fractures, arthritis, back pain, and sports injuries. But orthopedic surgeons are not just for broken bones—they help repair, replace, and restore function to the entire body’s framework. From simple sprains to complex joint replacements, they’re the experts who fix what keeps you moving.
They’re more than just doctors—they’re the architects of your physical motion.
Orthopedic surgery isn’t just about fixing fractures—it’s about restoring function
When you think of an orthopedic surgeon, you probably picture them setting a broken bone. But their work is much more than that. They also perform surgeries to correct deformities, treat chronic conditions, and help you regain lost mobility. Hip replacements, knee surgeries, spinal fusions, and even shoulder repairs fall under their expertise. The goal isn’t just to heal injuries—it’s to restore the way you move, live, and enjoy life.
Orthopedic surgeons don’t just heal—they rebuild the foundation of your body’s movement.
From sports injuries to wear-and-tear: They handle it all
An orthopedic surgeon treats a wide variety of conditions. For athletes, this might mean repairing torn ligaments, treating joint dislocations, or addressing fractures. For older adults, it could involve joint replacements, spine care, or managing arthritis. No matter the age or activity level, an orthopedic surgeon helps people continue to move without pain or restriction. The goal is to help you recover fully—whether you’re a professional athlete or simply want to enjoy a walk without discomfort.
They treat your body as a whole, not just the parts that are broken.
The process starts with an evaluation and ends with a treatment plan
When you see an orthopedic surgeon, the first step is an evaluation. This includes discussing your symptoms, medical history, and how the condition is affecting your daily life. They may take X-rays or other imaging tests to better understand the injury or condition. From there, they create a treatment plan that could include physical therapy, medication, or, if necessary, surgery. Not all orthopedic issues require surgery, and many are treated with non-invasive methods. Surgery is always the last resort, but when it’s needed, they know exactly how to proceed.
It’s about understanding the problem—and knowing when to act.
Surgery is often the solution—but it’s never the first step
While orthopedic surgeons are highly trained in surgery, they don’t jump to it immediately. Non-invasive treatments, such as physical therapy, braces, or injections, are often explored first. They may recommend lifestyle changes to reduce stress on a joint or muscle, like weight loss or activity modifications. Surgery is always the last option, used when other treatments have not been effective. For example, knee replacement surgery is typically considered only when other options, like physical therapy and injections, have not provided relief.
Surgery isn’t always the answer—but when it is, it’s life-changing.
A range of procedures: From minimally invasive to major operations
Orthopedic surgeons are skilled in various procedures, from minimally invasive arthroscopy to complex joint replacements. Minimally invasive surgeries use small incisions, allowing for faster recovery times and less pain. For example, knee and shoulder arthroscopies can be done using tiny cameras and instruments. In more severe cases, they may perform full joint replacements, like hip or knee surgery, or even complex spine surgeries. Depending on the procedure, recovery times vary, but orthopedic surgeons guide patients through each step, from pre-surgery prep to post-operative rehabilitation.
Whether it’s a small scope or a major operation, they tailor the procedure to the condition.
Joint replacements: A major part of orthopedic surgery
Joint replacement surgery is one of the most common procedures performed by orthopedic surgeons. This often involves replacing a damaged or worn-out joint, such as the hip, knee, or shoulder, with an artificial one. The goal is to relieve pain and restore mobility. Joint replacements are usually recommended for individuals who suffer from severe arthritis, joint degeneration, or injuries that have caused permanent damage. After the procedure, patients often experience significant pain relief and a return to regular activities.
Joint replacement can offer a fresh start when everything else fails.
Spine surgery: A delicate and complex area of orthopedic care
Spine surgery is another critical area of orthopedic surgery. The spine is complex, with many potential problems such as disc herniations, spinal stenosis, and fractures. Surgery might be required for conditions like chronic back pain, scoliosis, or other spinal deformities. These surgeries can range from minimally invasive techniques, such as microdiscectomy, to more complex procedures like spinal fusions. Spine surgery requires careful planning and precision, as the spine affects nearly every part of the body’s movement.
Spine surgery is a delicate balance of restoring function while avoiding damage to critical nerves.
Sports medicine: Keeping athletes in motion
Sports medicine is an important sub-specialty of orthopedics. Orthopedic surgeons who specialize in sports medicine work with athletes of all ages to treat injuries and prevent future problems. They repair damaged ligaments, tendons, muscles, and bones caused by sports-related injuries. From sprained ankles to torn ACLs, they know exactly how to get athletes back to the game. They also provide rehabilitation and injury prevention strategies, making sure that athletes return to their sport safely and effectively.
Sports medicine is about not just fixing injuries—but keeping you in the game longer.
Post-surgery recovery: The work isn’t over once the surgery is done
After surgery, the role of an orthopedic surgeon doesn’t end. In fact, it’s only just begun. A successful surgery is just the first step toward full recovery. Physical therapy is often needed to regain strength, mobility, and function. Your orthopedic surgeon works closely with you during your recovery, monitoring your progress and adjusting your treatment plan as necessary. This stage is just as important as the surgery itself, ensuring that the joint, bone, or tissue heals properly and that you regain full use of the affected area.
Recovery is a partnership between you and your orthopedic surgeon, guiding you every step of the way.
Prevention and long-term care: An orthopedic surgeon’s job doesn’t end with surgery
Even after surgery, your orthopedic surgeon helps you prevent future injuries. They provide advice on lifestyle changes, exercises, and protective gear to ensure long-term health. For example, they may recommend specific exercises to strengthen muscles around joints and prevent overuse injuries. They also educate patients on proper posture and body mechanics, so they can prevent additional wear and tear on their musculoskeletal system. The goal is to ensure that you stay healthy and active long after the treatment.
Prevention is just as important as treatment when it comes to maintaining healthy movement.
Orthopedic surgeons: More than just bone doctors
Orthopedic surgeons are sometimes referred to as “bone doctors,” but their work goes far beyond that. They deal with the entire musculoskeletal system—bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, and nerves. They not only repair damage caused by trauma but also manage chronic conditions like arthritis and degenerative diseases. Their goal is to help you move better, feel better, and lead a more active, pain-free life.
Orthopedic surgeons are healers of both the body’s structure and the movement that depends on it.